Radiation Pressure
Radiation Pressure: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Radiation Pressure for Complete Absorption, Radiation Pressure, Radiation Pressure for Partial Reflection and Partial Absorption, and Radiation Pressure for Complete Reflection.
Important Questions on Radiation Pressure
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries of power, the force exerted by it on the surface is
A beam of light with intensity and cross sectional area is incident on a fully reflective surface at angle . Then the force exerted by the beam on the surface is
A light of intensity incidents on a black surface of area . The radiation pressure on the surface is
A source of power emits photon which incident on a surface away out of which is reflected back, what is the radiation pressure on the surface?
A brilliant arc lamp delivers a luminous flux of to a absorber. The force due to radiation pressure is:
A point source of light emits isotropically with a power of . The light is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting circular surface of radius at a distance of from the source. The force exerted by light on the surface is
Speed of light
A laser pointer has an output power of and emits light of wavelength . if the beam from the pointer is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting mirror, the force exerted by the light beam on the mirror will be approximately,
Assertion Electromagnetic waves exert pressure, called radiation pressure. Reason This is because they carry energy.
A laser beam has an average power of . What will be the pressure exerted on a surface by this beam if the cross-sectional area is ? (Assume perfect reflection and normal incidence.)
An earth-orbiting satellite has a solar energy collecting panel with total area . If solar radiations are perpendicular and completely absorbed, the average force associated with the radiation pressure is
(Solar constant)
The incident intensity on a horizontal surface at sea level from sun is about . If of this intensity is reflected and is absorbed, then find the ratio of radiation pressure to atmospheric pressure at sea level
A perfectly absorbing surface intercepts a parallel beam of monochromatic light of power incident on it normally the force exerted by light beam on the surface is
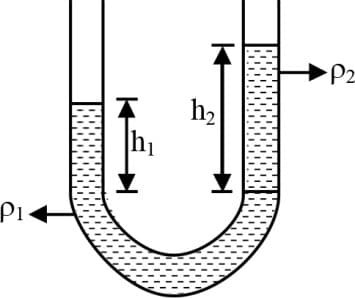
When two chemically non-reactive liquids are placed in a U-shaped tube as shown in the figure, then the heights of the liquid columns are,
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Electromagnetic waves carry energy as they travel through space and this energy is equally shared by the electric and magnetic fields.
Statement II: When electromagnetic waves strike a surface, a pressure is exerted on the surface.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
An object is placed in a medium of refractive index . An electromagnetic wave of intensity falls normally on the object and it is absorbed completely. The radiation pressure on the object would be (speed of light in free space ):
A laser beam of pulse power is focused on an object of area . The energy flux in at the point of focus is
A light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius . Assume that of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of chamber is perfectly absorbing. The pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber is
A parallel beam of light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries of power, the force exerted by it on the surface is
A radiation of is incident on a surface which is reflecting and absorbing. The total force on the surface is
A plane electromagnetic wave of intensity strikes a small mirror of area , held perpendicular to the approaching wave. The radiation force on the mirror will be
